Case Study
McCormack Innovation Ltd

Partners
University of Dundee
Sectors
Engineering and Technology
Life and Chemical Sciences
Regions
Fife
Background
Brian McCormack is a former coal miner turned inventor on a mission to improve cancer detection rates while helping the environment at the same time.
His company, McCormack Innovation Ltd, was initially set up to address the low return rates of bowel or colorectal cancer screening programmes worldwide where most return or compliance rates around a disappointing 50%. Harnessing soluble material as a solution and working in partnership with Smartsolve Industries based in Ohio, USA, the business has identified an ideal material to be used in stool sample collection that can then be harmlessly flushed away.
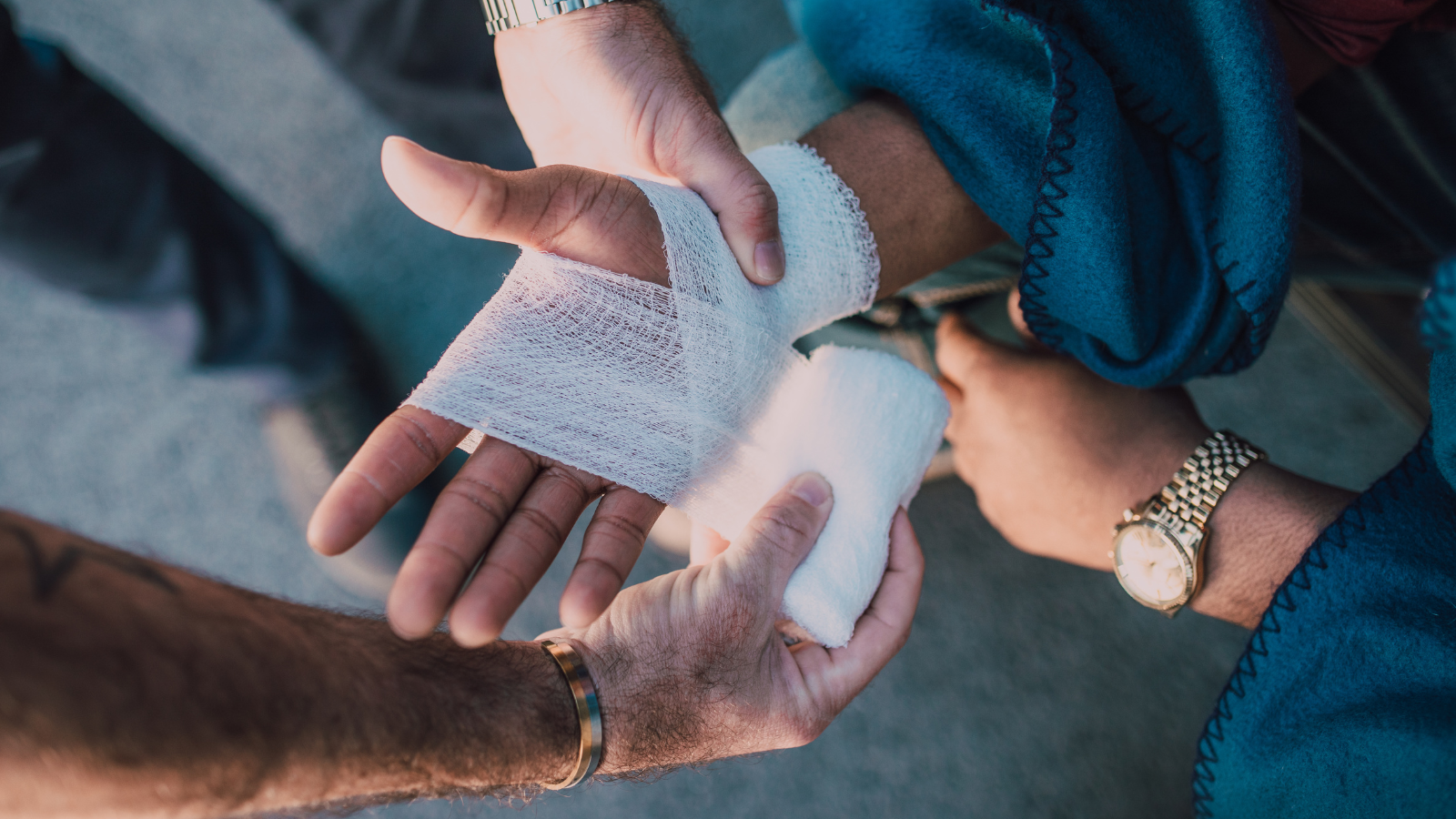
From their further research with similar “soluble” material, the idea to create an easily removed wound dressing came about. McCormack Innovation has patented an application for the FlushAway™ “soluble” wounds dressing. Using water dispersible material, these dressings can be used for burns units and patients with other ultrasensitive skin conditions like Epidermolysis Bullosa.
Challenge
There are presently many types of wound dressings on the market, even those described for use on sensitive skin. However, none of the current range of products include a wound dressing that is secure enough to complete the task yet can easily and painlessly be removed by showering or spraying with water. The FlushAway™ wound dressing addresses both these needs.
The business was looking to engage with academia to have the base material dermatologically tested and developed accordingly for market entry.
Solution
After being referred by Business Gateway in Fife, Interface was able to match the company with Professor Robert Keatch and Dr Jan Vorstius at the University of Dundee to undergo the following:
- Dermatological testing, highlighting any modifications required
- Ongoing development of the product for market entry
- Determining the appropriateness of the material and suggesting any improvements.
Specialist facilities at the University, along with access to clinicians and medical staff, were used for testing the biomaterials for use in the wound dressing.
In a product report, Professor Keatch and Dr Vorstius said: “All materials under test performed well, keeping their integrity and structure until exposed to water.
“The proposal to use this material as a secondary wound dressing would therefore be viable, providing the outer dressing can be kept dry until removal is required.
“This method would certainly reduce trauma inflicted during bandage removal and retain all the features of the conventional cotton and crepe bandages used.”
Benefits
The technical results from this project should help inform the further optimisation of the material for use in a number of medical applications. When ready for production, these innovative products will transform the market and bring about significant clinical improvements and patent relief at the point of care.
The company has been nominated for a large number of innovation awards, both nationally and internationally, and has been approached by some large biomedical companies interested in licensing the technology.